File sharing has become an essential part of modern digital life, enabling individuals and organizations to collaborate, share documents, and streamline workflows. However, this convenience also introduces significant security risks. Cybercriminals are increasingly exploiting file sharing platforms—both legitimate and rogue—to launch sophisticated attacks aimed at compromising devices and stealing sensitive information. Understanding how these platforms are weaponized is crucial for protecting yourself and your organization.
The Evolution of File Sharing Attacks
Traditionally, email providers like Gmail, Microsoft Outlook, and Yahoo Mail have relied on robust spam filters to scan incoming messages for suspicious attachments or links, marking them as spam to protect users. However, attackers are adapting. A new trend in phishing attacks involves using reputable file sharing platforms as the delivery mechanism for malicious content, bypassing traditional email security measures.
The Anatomy of a Modern File Sharing Attack
A typical attack scenario unfolds as follows:
- Step 1: Social Engineering
- The attacker crafts a convincing email, often impersonating a trusted colleague, business partner, or service provider. Instead of attaching a file directly, the email contains a link to a shared document hosted on a file sharing platform such as ZoopSign, Dropbox, or Google Drive.
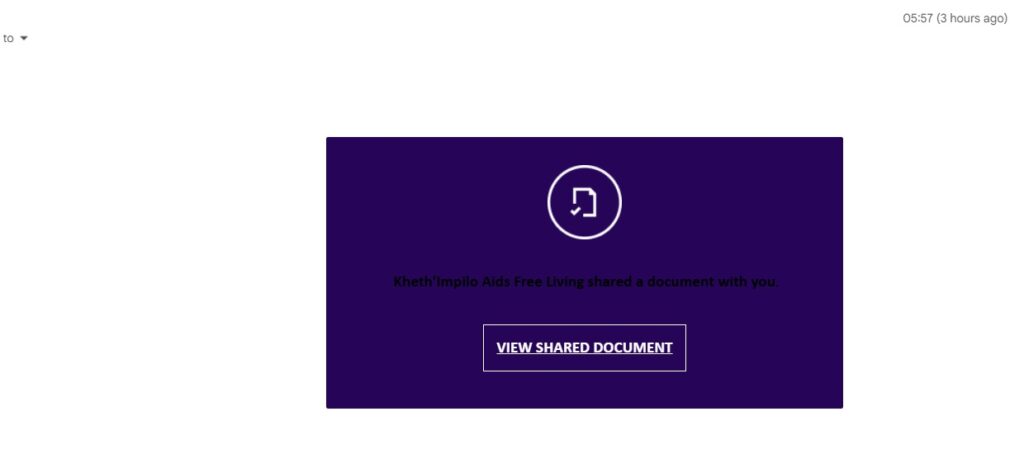
- Step 2: Redirect to Platform
- When the recipient clicks the link, they are redirected to the file sharing platform. In the case of platforms like ZoopSign, the user may be prompted to enter their name or other identifying information to access the document.
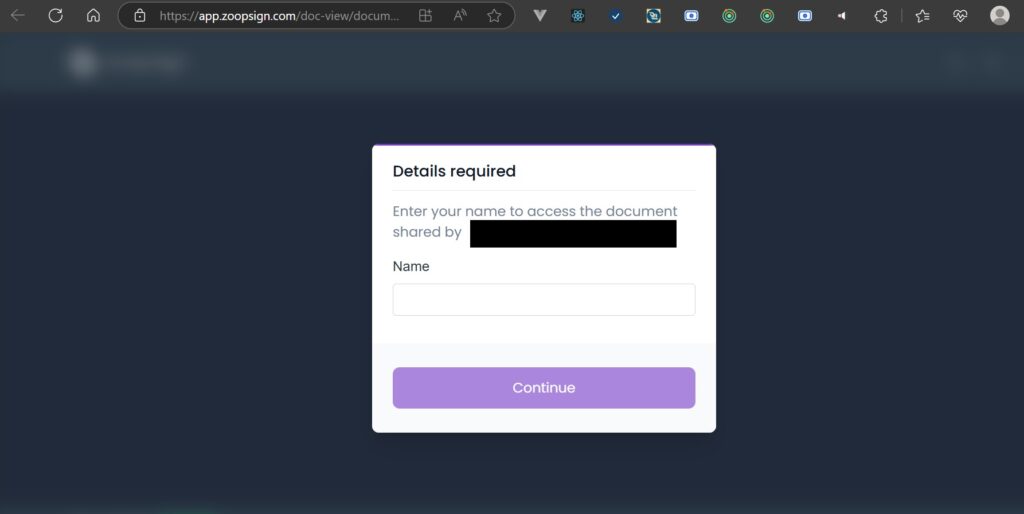
- Step 3: Delivery of Malicious Content
- Once inside, the platform displays a document—often a PDF—that appears legitimate. However, this document contains links to external websites or embedded executables. Clicking these links or downloading the embedded files can result in the installation of malware, ransomware, or remote access tools on the user’s device.
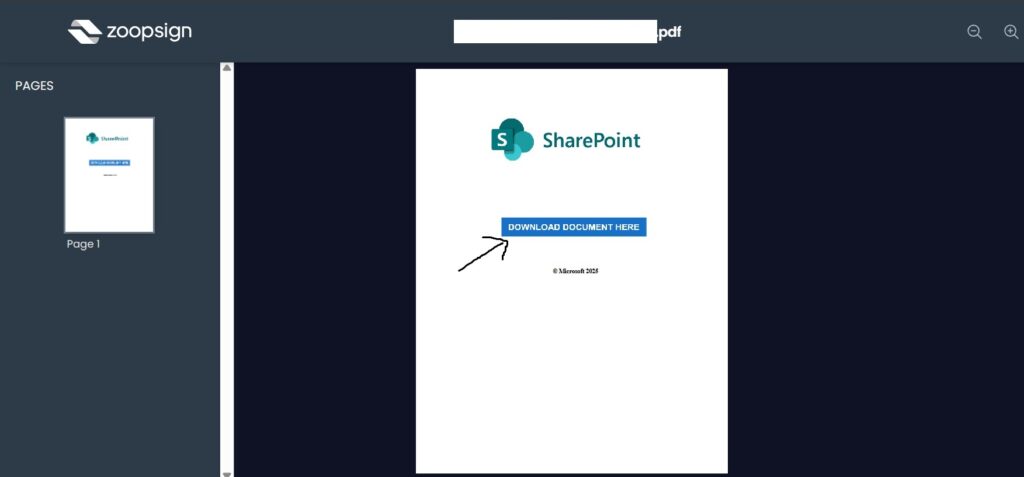
Why File Sharing Platforms Are Targeted
1. Trust and Familiarity
Users are more likely to trust links to well-known file sharing services, making them less suspicious and more likely to interact with the content.
2. Bypassing Email Filters
Since the actual malicious payload is hosted externally, traditional email security tools may not detect the threat, allowing the phishing email to reach the inbox.
3. Exploiting Platform Features
Many file sharing platforms offer features such as password protection, access controls, and document tracking. While these are designed for security, attackers can exploit them to create a false sense of legitimacy or to restrict access to only targeted victims.
Common File Sharing Security Risks
Malware Distribution
Attackers use file sharing to distribute viruses, worms, spyware, and Trojan horses. Opening a compromised file can infect not only the user’s device but also the broader network, especially in enterprise environments.
Data Leakage and Unauthorized Access
Weak access controls or misconfigured sharing settings can expose sensitive documents to unauthorized users. Attackers may exploit these vulnerabilities to gain access to confidential data or to escalate their privileges within an organization.
Phishing and Credential Theft
File sharing links are frequently used in phishing campaigns to harvest login credentials. Victims may be prompted to enter their username and password on a fake login page, handing their credentials directly to the attacker.
Shadow IT
Employees using unauthorized file sharing tools (shadow IT) can inadvertently create security gaps. These platforms may lack enterprise-grade security features, making them easy targets for cybercriminals.
Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
Unencrypted file transfers, especially over public Wi-Fi, can be intercepted by attackers using packet sniffing tools. This allows them to steal sensitive information or inject malicious files into the transfer stream.
Case Study: ZoopSign and the Double-Edged Sword of Security
Platforms like ZoopSign are designed with security in mind, offering advanced encryption, customizable access controls, and document tracking features. These measures are intended to protect sensitive information and ensure that only authorized users can access documents. However, attackers can exploit these same features to lend credibility to their phishing attempts.
For example, a phishing email may direct a user to a ZoopSign document, where the platform’s legitimate branding and security prompts reduce suspicion. Once the user enters their information and opens the document, they may encounter a malicious link or executable disguised as a contract or invoice. Despite ZoopSign’s robust security, the platform cannot prevent users from clicking on malicious links embedded within uploaded documents.
The Broader Impact: Risks to Businesses and Individuals
Regulatory and Compliance Risks
Industries such as healthcare, finance, and legal services are subject to strict regulations regarding data protection. Failure to secure file sharing can result in legal penalties, financial losses, and reputational damage.
Persistent Threats from Inactive Accounts
Organizations often overlook the need to revoke access for former employees or vendors. Inactive accounts with outdated credentials can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access to sensitive files.
Exposure of Personal and Confidential Information
Accidental file sharing or misconfigured permissions can expose entire directories or sensitive folders, making it difficult to track what information has been accessed or stolen.
How to Protect Yourself and Your Organization
1. Educate Users
Regularly train employees to recognize phishing attempts, suspicious links, and the risks associated with file sharing platforms.
2. Implement Strong Access Controls
Restrict access to sensitive documents using role-based permissions and regularly audit who has access to what.
3. Use Secure Platforms
Choose file sharing solutions that offer end-to-end encryption, password protection, and detailed audit logs. Avoid using unauthorized or consumer-grade platforms for business-critical data.
4. Keep Software Updated
Ensure that all devices and applications are updated with the latest security patches to defend against evolving threats.
5. Monitor and Revoke Access
Regularly review and revoke access for inactive users or external vendors to minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
6. Avoid Public Wi-Fi for Sensitive Transfers
Discourage employees from accessing or transferring sensitive files over public Wi-Fi networks to prevent interception by cybercriminals.
Conclusion
File sharing platforms are indispensable tools for modern collaboration, but their convenience comes with significant security risks. Attackers are increasingly leveraging these platforms to bypass traditional defenses and target unsuspecting users with sophisticated phishing and malware campaigns. By understanding the tactics employed by cybercriminals and adopting robust security practices, individuals and organizations can mitigate the risks and safely harness the benefits of file sharing technology.
